With GitHub
Use GitHub as a remote content source
Experimental
It might be unstable.
MDX Remote offers a GitHub integration, it allows you to use a GitHub repository as the content source of your documentation.
When to use it?
When your docs site is too large for the built-in content sources (e.g. Fumadocs MDX), building all pages in build time takes too much time. For example, you have a docs with more than 1000 MDX files under the project.
For smaller docs, Fumadocs MDX may be a better option.
Features
With MDX Remote GitHub, in production, your documentation will be automatically updated whenever you make changes to the content in your GitHub repository.
You don't need to re-build or re-deploy the entire docs site when the content updates.
Setup
In source.ts, change the usage of loader to:
Then, change all usages to the original output to await getDocs().
The createSourceAuto function fetches the file tree (file structure), which is required to generate the page tree.
Depending on the environment (process.env.NODE_ENV):
| Environment | Source |
|---|---|
| Production | use the GitHub API and fetch Git Tree. |
| Development | use the file system directly. |
To dedupe the requests, we will use React cache.
Force a Source?
You can use the from option to force a source.
Be careful, this may break the MDX Remote development server.
Hot Reload
MDX Remote provides a development server for implementing hot reload under development environments. It uses a file watcher to detect for local content changes, and notify the client via WebSocket.
Initialize the server in your next.config.mjs:
Add the hot reload component to client, it's recommended to add it to a layout.
Page
In your docs page, you have to manually resolve the file content, and compile it using the built-in MDX Compiler.
Search
MDX Remote provides a simple way to build search indexes. It should be executed every time the content is changed to ensure search indexes are up-to-date.
Deploy
MDX Remote GitHub uses Webhook to receive notifications from GitHub and revalidates cache.
In the settings of your GitHub repository, go to the Webhook Tab and create a new Webhook:
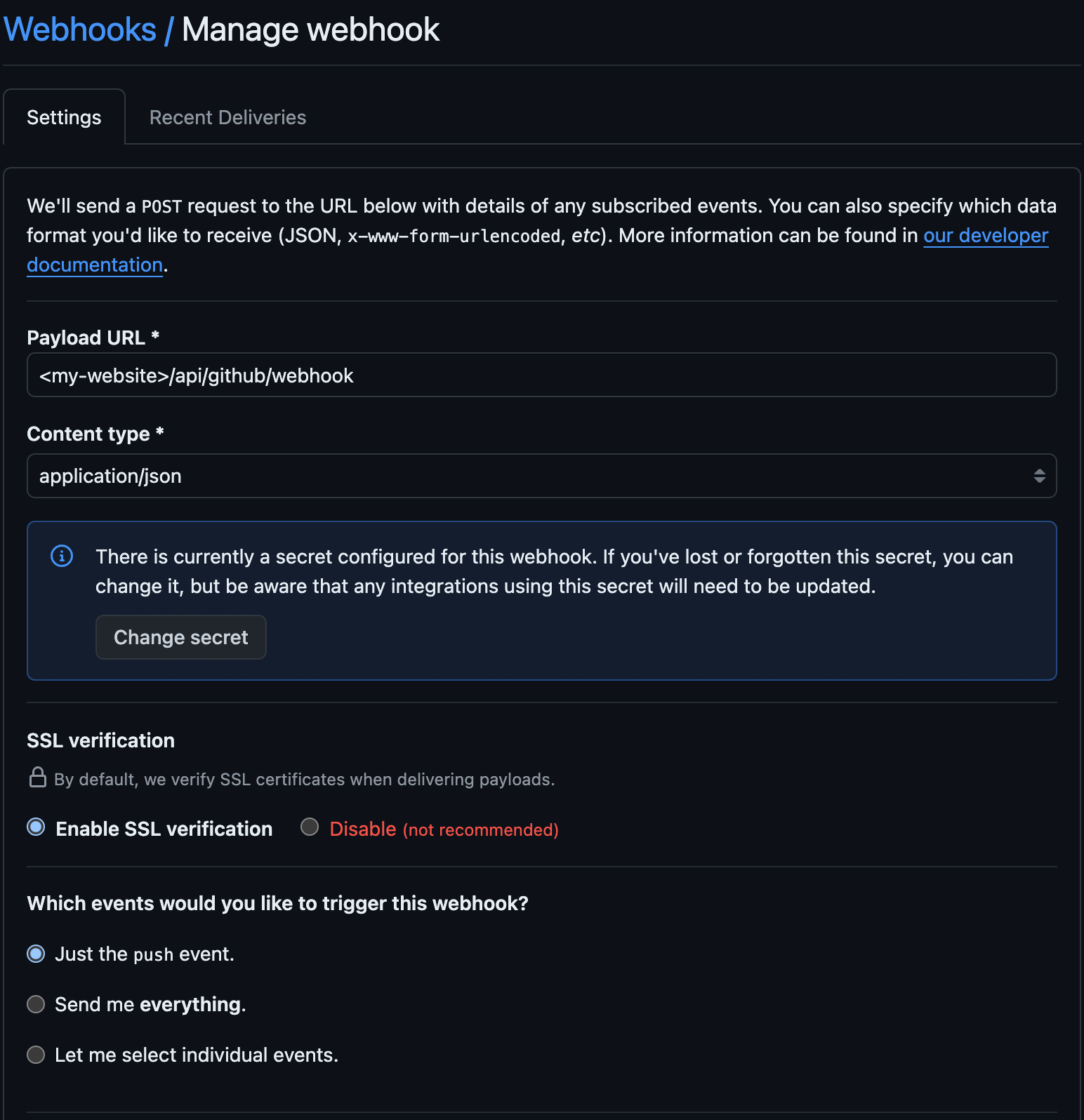
Remember to give it a secret, it will be used later.
In your app, add the following route handler.
Now you can deploy your app.
For projects hosted on Vercel, or other platforms which provides a GitHub integration, skip the deployment step when the commit only affects your content. Otherwise, the optimization of MDX Remote cannot take effect.
On Vercel, this can be done with Ignore Build Step.
Deep Dive
Internally, we use the Next.js cache. It allows us to incrementally update the documentation in real-time, avoiding rebuilding the entire documentation every time a change is made.
Last updated on
